

This table shows how shapefile feature classes are converted to geodatabase geometry.Įach shapefile and dBASE field type converts to a single geodatabase field type, except for the Number type field. Therefore, importing shapefile datasets into geodatabases is relatively straightforward.Īll feature types in shapefiles convert to geometry types in the geodatabase as denoted in the following table. The geometry types for points, lines, and polygons in Esri shapefiles are similar to the corresponding geodatabase feature class types. This section describes how shapefiles are converted into geodatabase content. When you import shapefiles and dBASE tables into the geodatabase, ArcGIS automatically converts the shapefile geometry and fields to types used by the geodatabase. If the coverage you're importing doesn't use the field to relate to another table, don't import this field.When importing line coverages, don't import, RPOLY#, LPOLY#, FNODE, TNODE, or LENGTH.When importing polygon or point coverages, don't import, AREA, or PERIMETER.The following is recommended in most cases: The following table summarizes how items convert.Ĭoverages contain several fields that are relevant to the coverage data model only and are not maintained by the geodatabase therefore, you should determine if you want to import them. For example, you can map an item type to a short integer, long integer, or double, depending on its width. Coverage and INFO table items convert based on a combination of their type and width. This table illustrates how feature class types convert to geodatabase geometry types.Īll attribute types in coverages and INFO tables convert to field types in the geodatabase. The following table illustrates how feature class types convert to geodatabase geometry types. For example, point feature classes, tic feature classes, and node feature classes all convert to separate point feature classes in the geodatabase. Each coverage feature class becomes a new geodatabase feature class. This section describes how coverages are converted into geodatabase content.Īll feature class types within ArcGIS Desktop Advanced coverages convert to one of four fundamental geometry types in the geodatabase (points, lines, polygons, or annotation). When you import coverages and INFO tables into the geodatabase, ArcGIS automatically converts the coverage geometry and fields to types used by the geodatabase. Importing ArcGIS Desktop Advanced coverages
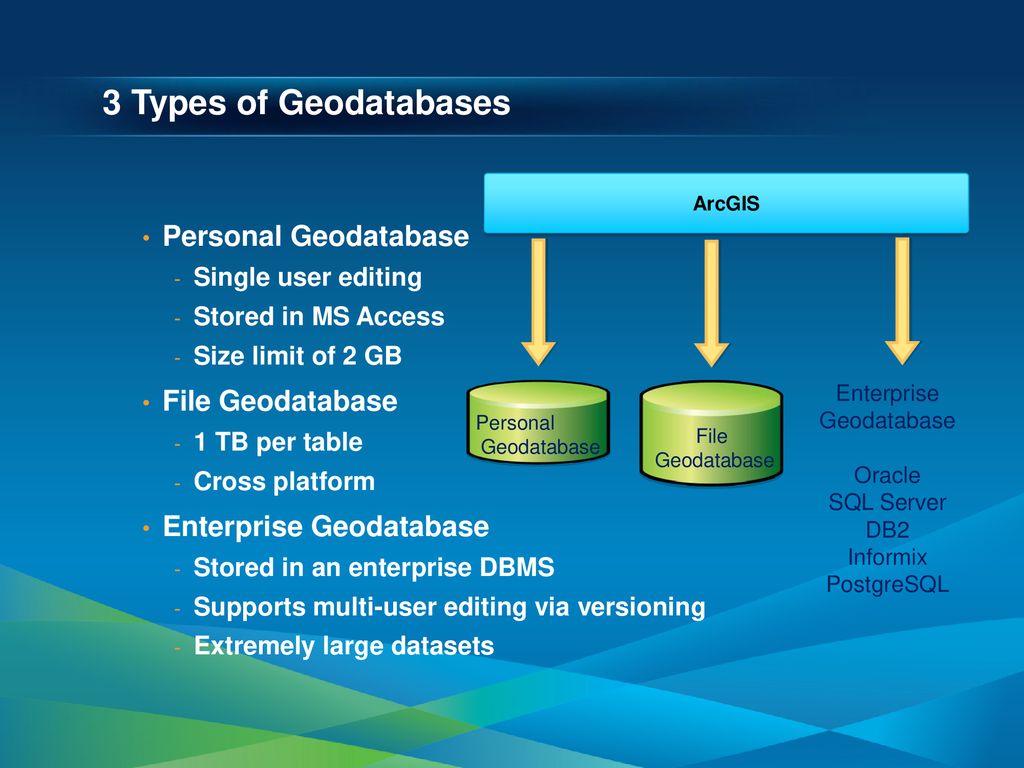
The following describes how different formats are converted during the importing process. When you import data that is in a format not used by the geodatabase, ArcGIS automatically converts it into data types used by the geodatabase. Importing existing data into the geodatabase.Importing ArcGIS Desktop Advanced coverages.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
